How to Load Tissue Paper Mother Rolls into a Container for Sea Shipping?
When it comes to transporting tissue paper mother rolls via sea shipping, careful planning and execution are critical. The delicate nature of these rolls, combined with their bulk and weight, necessitates a specialized approach to loading them into containers. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to load tissue paper mother rolls into a container for sea shipping, ensuring both safety and efficiency.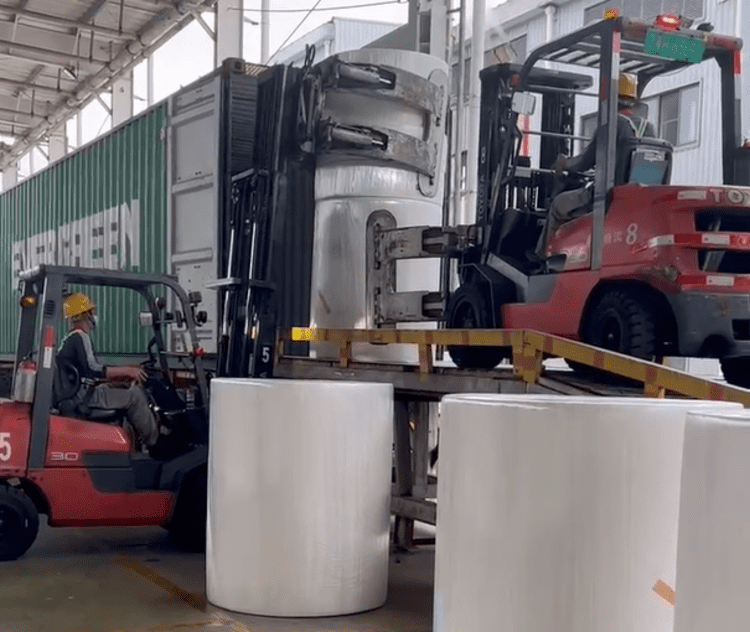
1. Overview of Tissue Paper Mother Roll Loading for Sea Shipping
Tissue paper mother rolls, also known as parent rolls, are large, cylindrical rolls of paper used in various downstream applications. Given their size and weight, improper handling during loading can result in product damage, accidents, or even loss during transit. This guide focuses on the best practices for loading these rolls into shipping containers, emphasizing both the efficiency of space utilization and the safety of the loading process.
2. Importance of Proper Loading Techniques
The correct loading of tissue paper mother rolls into containers is essential for several reasons:- Product Integrity: Ensuring that the rolls arrive at their destination without damage is crucial for maintaining product quality.
- Maximizing Space: Efficient use of container space reduces shipping costs by allowing more rolls to be transported in a single shipment.
- Safety: Proper loading techniques help prevent accidents and injuries during both the loading and unloading processes.
3. Placement of Tissue Paper Mother Rolls in the Container
3.1. Stacking Orientation
The orientation of the rolls during loading is a key factor in maximizing space and ensuring stability.3.1.1. Upright Vertical Stacking
- Single Layer Vertical Stacking: In this method, each tissue paper roll is placed upright, directly on the container floor. This technique is commonly used for larger rolls where only a single layer can be accommodated. It minimizes the risk of rolls toppling over during transit.
- Multi-Layer Vertical Stacking: This involves stacking two or more layers of rolls vertically. This method is more space-efficient and is suitable for rolls of moderate size. Care must be taken to ensure that the rolls are securely stacked to prevent movement during shipping.
3.1.2. Horizontal Stacking
- Single Layer Horizontal Stacking: Rolls are laid flat on the container floor, side by side, in a single layer. This method is often used for smaller rolls or when vertical space in the container is limited.
- Multi-Layer Horizontal Stacking: Similar to the single layer method, but with additional layers stacked horizontally. This approach is useful for maximizing container space, especially with smaller diameter rolls.
3.1.3. Staggered Stacking
- Alternating Vertical and Horizontal Stacking: This method alternates between vertical and horizontal layers, providing a balance between space utilization and stability. It is particularly effective for long-distance shipping where roll stability is a concern.
3.1.4. Inclined Stacking
- Angled Inclined Stacking: Rolls are placed at an angle within the container. This less common method is used for specific container types or when handling non-standard roll sizes. It requires precise planning to avoid space wastage and ensure load stability.
3.2. Arrangement of Rolls
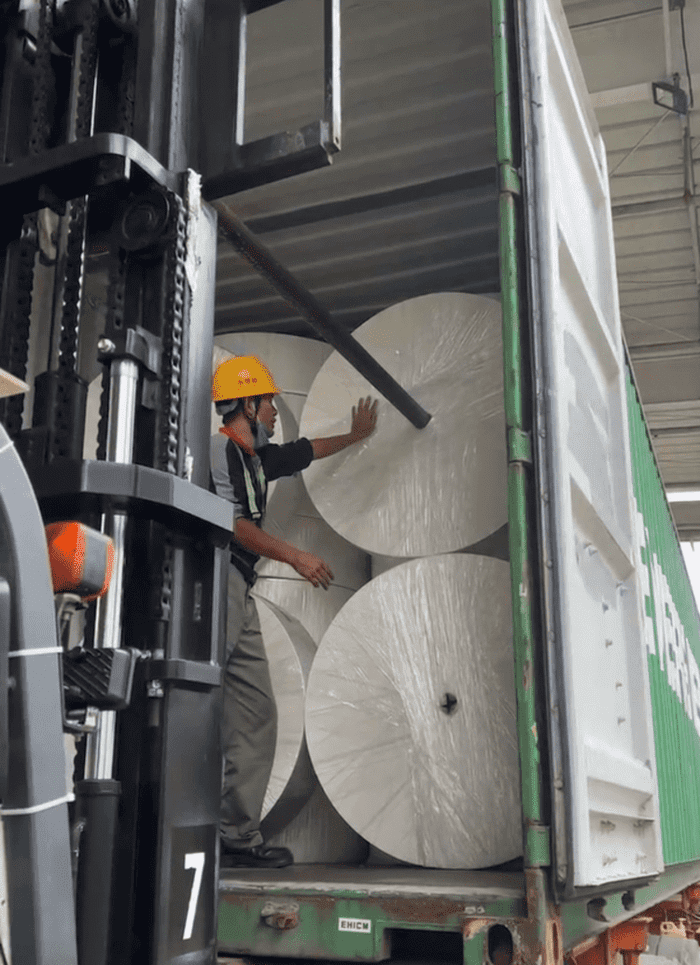
- Once the stacking orientation is chosen, the rolls must be tightly packed to prevent any movement during transit. The arrangement should minimize gaps between rolls, as these gaps can lead to shifting, which may cause damage to the rolls or even lead to accidents.
3.3. Container Filling
- Layered Loading: The loading process typically begins at the back of the container, with rolls placed in layers. Each subsequent layer is added on top of the previous one until the container is full. This method ensures an even distribution of weight across the container, reducing the risk of tipping.

4. Handling Tools for Loading Tissue Paper Mother Rolls
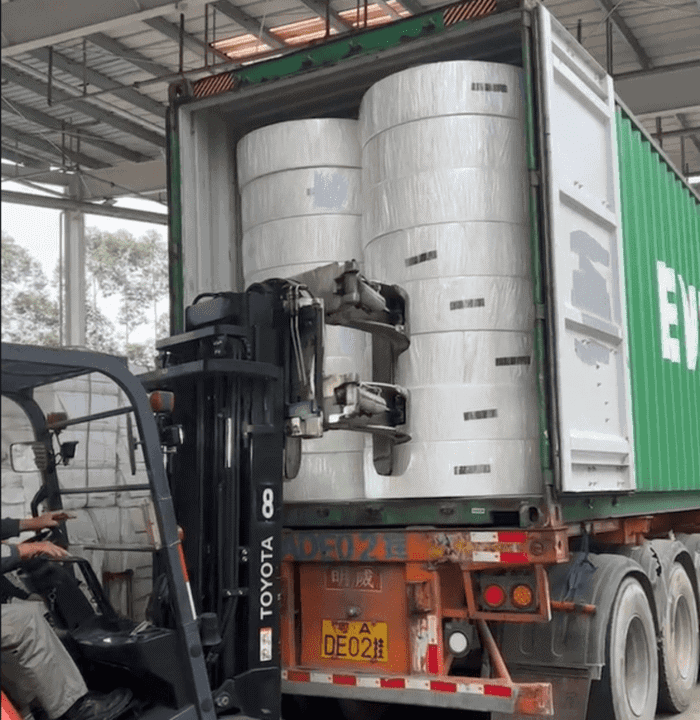
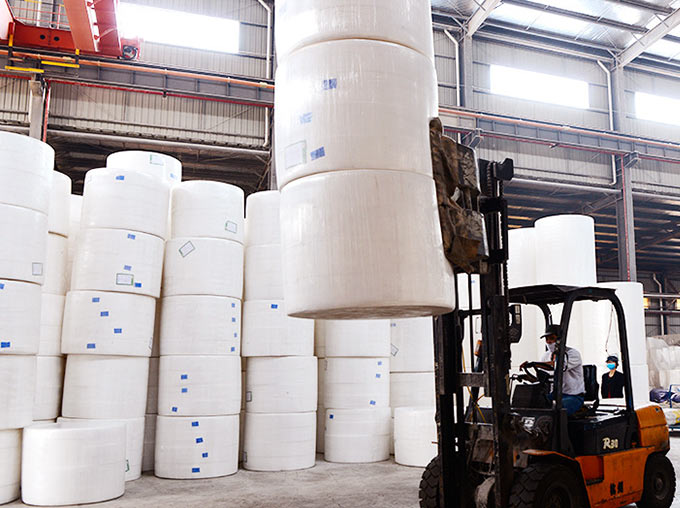
4.1. Forklift Use
Forklifts equipped with specialized roll clamps are the primary tools used for handling tissue paper mother rolls during the loading process.- Roll Clamps: These clamps are designed to grip the rolls securely without damaging the paper. The clamp pressure should be carefully adjusted based on the size and weight of the rolls to ensure a firm hold while preventing any crushing of the material.
4.2. Handling Precision
Forklift operators must handle the rolls with precision, especially when positioning them within the container. Misalignment or improper placement can lead to instability and potential damage during transit.- Operator Coordination: Effective communication between forklift operators and workers inside the container is essential. A worker inside the container should guide the forklift operator to ensure that each roll is correctly aligned and securely positioned.
4.3. Loading Coordination
The loading process should be well-coordinated to maintain efficiency and safety. Proper planning ensures that the container is filled optimally, with no wasted space or unnecessary handling of the rolls.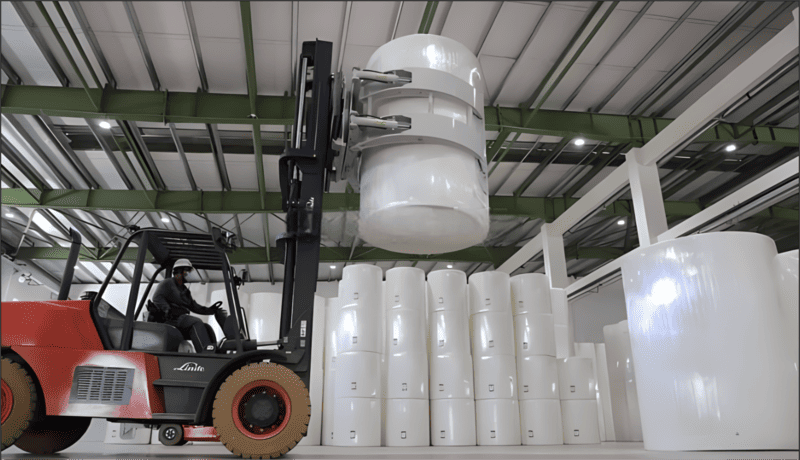
5. Safety Considerations During Loading
Safety is a paramount concern when loading tissue paper mother rolls into a container. The following safety measures should be adhered to:5.1. Operator Safety
- Protective Gear: Forklift operators and workers involved in the loading process should wear appropriate safety gear, including helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots. This gear protects them from potential injuries caused by accidental roll movements or equipment malfunctions.
5.2. Load Stability
- Constant Monitoring: The stability of the stacked rolls should be constantly monitored throughout the loading process. Any sign of instability should be addressed immediately to prevent accidents.
- Securing Rolls: In some cases, it may be necessary to use straps or other securing devices to keep the rolls in place, especially if the container is not fully packed or if the rolls are smaller in diameter.
5.3. Even Weight Distribution
- Balanced Loading: Rolls should be evenly distributed throughout the container to ensure that the weight is balanced. Uneven weight distribution can lead to container tipping, especially during loading and unloading operations.
- Side-to-Side and Front-to-Back Balance: Attention should be given to both the side-to-side and front-to-back balance of the container load. This helps in maintaining stability during transport, particularly in rough sea conditions.
6. Conclusion
The proper loading of tissue paper mother rolls into containers for sea shipping is a meticulous process that requires careful attention to detail. By following the best practices outlined in this guide—such as choosing the correct stacking orientation, using appropriate handling tools, and adhering to safety protocols—you can ensure that the rolls are transported safely and efficiently. Proper loading not only protects the product from damage but also contributes to the overall safety and success of the shipping operation.FAQ
1. What is the best stacking method for tissue paper mother rolls?
The best stacking method depends on the roll size and container dimensions. Vertical stacking is commonly used for larger rolls, while horizontal stacking is suitable for smaller rolls.
2. How do I ensure the rolls don’t move during transit?
Tightly pack the rolls with minimal gaps between them, and use securing devices like straps if necessary to prevent shifting.
3. Can tissue paper rolls be damaged during loading?
Yes, improper handling or incorrect clamp pressure can damage the rolls. Ensure that forklift operators use appropriate handling techniques.
4. What safety gear should workers wear during loading?
Workers should wear helmets, gloves, and steel-toed boots to protect against potential injuries during the loading process.
5. How important is weight distribution in the container?
Even weight distribution is crucial for preventing container tipping and ensuring stability during transport.
6. Is it necessary to coordinate loading with workers inside the container?
Yes, coordination between forklift operators and inside workers is essential for proper roll alignment and secure placement.