Mechanical Pulping vs. Chemical Pulping
Which is the better pulping method for Papermaking?
Paper is one of the most widely used materials in the world, with applications ranging from writing and printing to packaging and hygiene. Paper is made from cellulose fibers that are extracted from wood or other plant sources. The process of extracting and preparing these fibers for paper production is called pulping.
Pulping is a crucial step in the papermaking industry, as it determines the quality, characteristics, and cost of the final paper product. There are two primary methods of pulping: mechanical and chemical. These methods differ in how they separate the fibers from the lignin, which is the glue-like substance that binds the fibers together in the wood structure.
In this article, we will explain the differences between mechanical and chemical pulping, their advantages and disadvantages, their typical applications, and their future prospects.
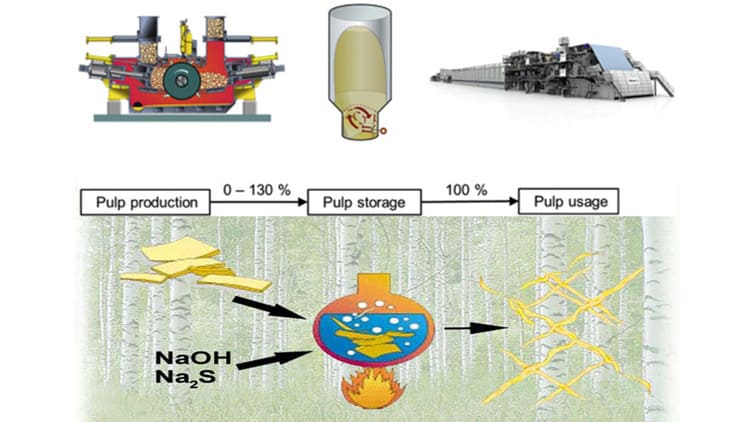
What are Pulping of Paper making process?
Pulping is the process of breaking down wood or other plant materials into a pulp, which is a mixture of water and fibers. The purpose of pulping is to free the fibers from the lignin and other impurities that cause discoloration and degradation of the paper. Pulping also modifies the properties of the fibers, such as their length, strength, flexibility, and bonding potential.
The raw materials used for pulping are mainly wood chips or logs, but other sources of cellulose fibers can also be used, such as straw, bamboo, cotton, hemp, or recycled paper. The choice of raw material depends on factors such as availability, cost, quality, and environmental impact.
Mechanical Pulping
Mechanical pulping is a method of pulping that uses physical force to separate the fibers from the lignin. The wood chips or logs are subjected to an abrading action, either by pressing them against a revolving grinding stone or by passing them through a mill. The wood fibers are separated and fragmented by the mechanical action, but most of the lignin remains attached to them.
There are three main types of mechanical pulping processes:
- Groundwood process: This is the simplest and oldest form of mechanical pulping. The wood logs are pressed against a rotating stone that grinds them into pulp. The pulp has a high yield (about 95%) but low strength and brightness.
- Thermomechanical process (TMP): This is an improved version of groundwood pulping that uses heat and steam to soften the wood before grinding it. The pulp has a higher strength and brightness than groundwood pulp, but lower than chemical pulp.
- Chemi-Thermomechanical process (CTMP): This is a hybrid process that combines mechanical and chemical treatments. The wood chips are pretreated with chemicals (such as sodium sulfite) to partially dissolve the lignin before grinding them. The pulp has a higher strength and brightness than TMP pulp, but lower than chemical pulp.
Advantages of Mechanical Pulping
Mechanical pulping has some advantages over chemical pulping, such as:
- High yield: Mechanical pulping uses almost all of the wood material, resulting in a high yield of pulp (about 90-95%). This means less waste and lower raw material costs.
- Low cost: Mechanical pulping requires less energy and chemicals than chemical pulping, making it cheaper to operate.
- Energy efficiency: Mechanical pulping generates heat during the grinding process, which can be used to produce steam or electricity for the mill.
Disadvantages of Mechanical Pulping
Mechanical pulping also has some disadvantages compared to chemical pulping, such as:
- Lower strength papers: Mechanical pulp contains a lot of lignin, which makes the fibers stiff and brittle. This reduces the strength and flexibility of the paper produced from mechanical pulp.
- Lower brightness levels: Mechanical pulp has a dark color due to the presence of lignin and other impurities. This makes it unsuitable for producing white or bright papers.
- Limited lifespan: Mechanical pulp is prone to yellowing and deterioration over time due to the oxidation of lignin by light and air. This limits its use for archival or long-lasting papers.
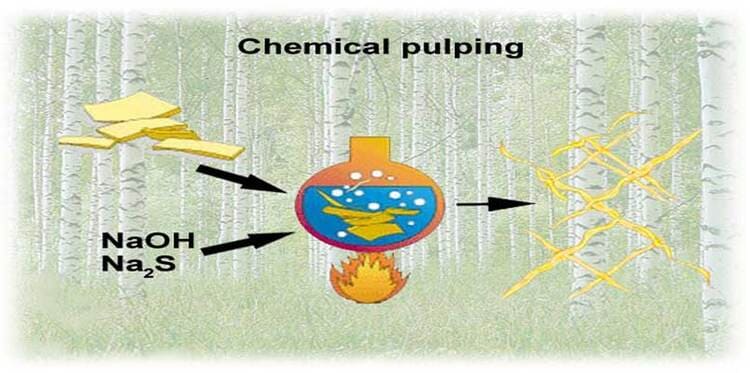
Chemical Pulping
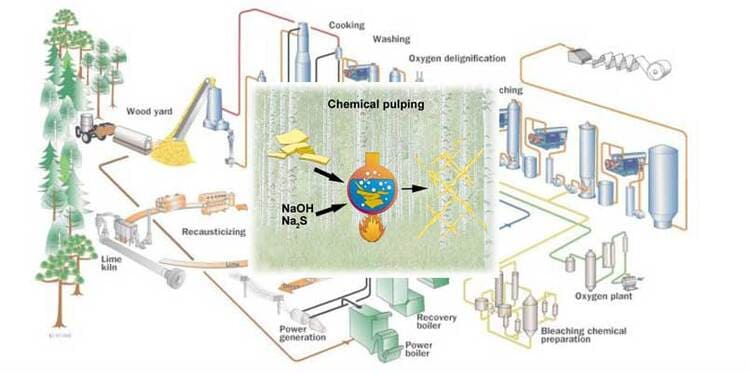
Chemical pulping is a method of pulping that uses chemical solutions to dissolve the lignin and separate the fibers from each other. The wood chips are cooked in digesters with chemicals at high temperature and pressure. The lignin is made soluble by the chemicals and removed from the pulp by washing or bleaching.
There are three main types of chemical pulping processes:
- Kraft (sulfate) process: This is the most common and widely used chemical pulping process. The wood chips are cooked with a solution of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide, which dissolves the lignin and produces a strong and versatile pulp. The pulp has a low yield (about 45-50%) but high strength and brightness.
- Sulfite process: This is an older and less popular chemical pulping process. The wood chips are cooked with a solution of sulfurous acid and calcium, magnesium, sodium, or ammonium bisulfite, which dissolves the lignin and produces a pulp that is suitable for fine papers. The pulp has a higher yield (about 50-55%) but lower strength and brightness than kraft pulp.
- Soda process: This is a simple and cheap chemical pulping process that uses only sodium hydroxide as the cooking agent. The pulp has a low yield (about 35-40%) and low strength and brightness, but it is easy to bleach and can be used for specialty papers.
Advantages of Chemical Pulping
Chemical pulping has some advantages over mechanical pulping, such as:
- Higher strength papers: Chemical pulp contains very little lignin, which makes the fibers flexible and resilient. This increases the strength and durability of the paper produced from chemical pulp.
- Greater longevity: Chemical pulp is resistant to yellowing and degradation over time due to the removal of lignin and other impurities. This makes it suitable for producing archival or long-lasting papers.
- Brighter papers: Chemical pulp has a light color due to the removal of lignin and other impurities. This makes it suitable for producing white or bright papers.
Disadvantages of Chemical Pulping
Chemical pulping also has some disadvantages compared to mechanical pulping, such as:
- Lower yield: Chemical pulping uses only a fraction of the wood material, resulting in a low yield of pulp (about 40-55%). This means more waste and higher raw material costs.
- Environmental concerns: Chemical pulping generates a lot of pollutants, such as organic compounds, sulfur compounds, and black liquor, which need to be treated or disposed of properly. Chemical pulping also consumes more water and energy than mechanical pulping.
- Higher cost: Chemical pulping requires more energy and chemicals than mechanical pulping, making it more expensive to operate.

Comparison between Mechanical and Chemical Pulping
The following table summarizes the main differences between mechanical and chemical pulping in terms of yield, cost, quality of paper, and environmental impact.
| Aspect | Mechanical Pulping | Chemical Pulping |
| Yield | High (90-95%) | Low (40-55%) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Quality of paper | Low strength, low brightness, limited lifespan | High strength, high brightness, greater longevity |
| Environmental impact | Low pollution, low water consumption, high energy efficiency | High pollution, high water consumption, low energy efficiency |
Application and Use Cases
Mechanical and chemical pulps have different applications and use cases depending on their properties and characteristics.
Typical use cases of mechanically pulped paper
Mechanically pulped paper is mainly used for products that do not require high strength or brightness, such as:
– Newsprint
– Magazines
– Catalogs
– Books
– Tissue paper
– Paperboard
Typical use cases of chemically pulped paper
Chemically pulped paper is mainly used for products that require high strength or brightness, such as:
– Writing paper
– Printing paper
– Copy paper
– Envelopes
– Labels
– Fine paper
– Specialty paper
Future of Papermaking and Pulping
Papermaking and pulping are constantly evolving fields that are influenced by various factors, such as consumer demand, technological innovation, environmental regulations, and market competition. Some of the current trends and innovations in pulping techniques are:
- Recycled pulp: Recycled pulp is made from recovered paper that is deinked and refined to produce new paper. Recycled pulp reduces the need for virgin wood fibers and saves resources and energy. Recycled pulp can be mixed with mechanical or chemical pulp to produce various grades of paper.
- Biorefinery concept: Biorefinery concept is an integrated approach that aims to utilize all components of the biomass in an efficient way. Biorefinery concept involves converting the lignin and hemicellulose fractions of the wood into valuable products, such as biofuels, bioplastics, biochemicals, or biomaterials. Biorefinery concept enhances the profitability and sustainability of the pulp and paper industry.
- Nanocellulose: Nanocellulose is a novel material that consists of cellulose nanofibers or nanocrystals that have unique properties, such as high strength, high surface area, high biodegradability, and high optical transparency. Nanocellulose can be used to enhance the oxygen and water vapor barrier properties of the packaging materials when used as a coating, fillers in composites, and as self-standing thin films.

Conclusion
Mechanical and chemical pulping are the two primary processes in papermaking that differ in how they separate the fibers from the lignin in the wood. Mechanical pulping uses physical force to grind the wood, while chemical pulping uses chemical solutions to dissolve the lignin. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of yield, cost, quality of paper, and environmental impact.
Mechanical pulping produces a high yield of pulp with low cost and low pollution, but it also produces low strength, low brightness, and limited lifespan papers. Chemical pulping produces a low yield of pulp with high cost and high pollution, but it also produces high strength, high brightness, and greater longevity papers.
The choice between mechanical and chemical pulping depends on the desired properties and applications of the final paper product. Mechanical pulping is suitable for products that do not require high strength or brightness, such as newsprint, magazines, or paperboard. Chemical pulping is suitable for products that require high strength or brightness, such as writing paper, printing paper, or fine paper.
Papermaking and pulping are dynamic and evolving fields that are influenced by various factors, such as consumer demand, technological innovation, environmental regulations, and market competition. Some of the current trends and innovations in pulping techniques are recycled pulp, biorefinery concept, and nanocellulose. These techniques aim to enhance the profitability and sustainability of the pulp and paper industry by utilizing the biomass more efficiently and creating new products with novel properties.
Paper is a versatile and essential material that has many uses and benefits for society. By understanding the differences between mechanical and chemical pulping, we can appreciate the diversity and complexity of paper production and make informed decisions about its consumption and conservation.